
The Alchemist
¥8.09
The Alchemist

Musical Memories
¥8.09
Musical Memories

Chopin and Other Musical Essays
¥8.09
Chopin and Other Musical Essays
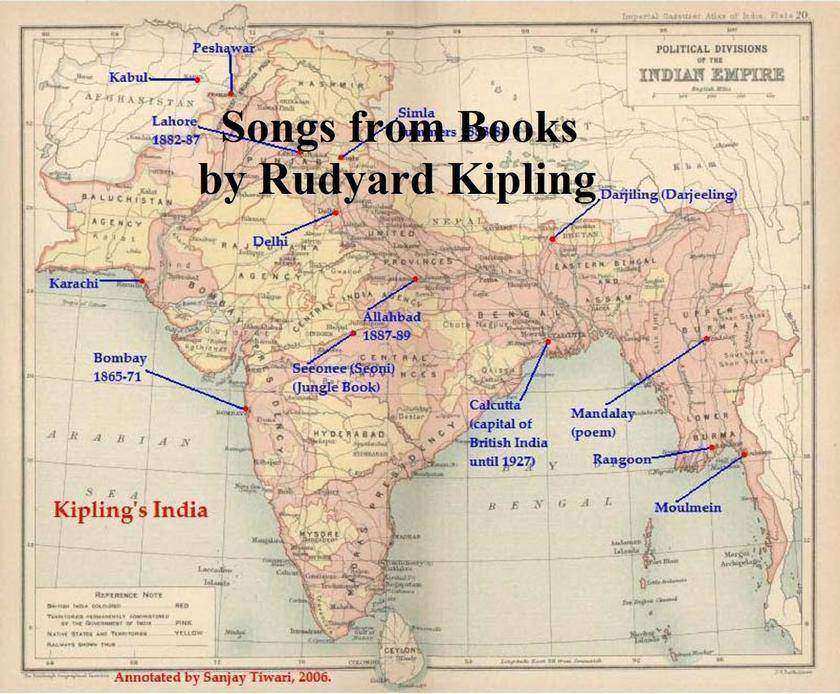
Songs from Books
¥8.09
Songs from Books

Two Books of Poetry
¥8.09
This file includes: "Green Helmet and Other Poems" (first published in 1911) and In the Seven Woods: being poems chiefly of the Irish heroic age" (first published in 1903). The active table of contents has links to each poem. The verse plays "The Green Helmet, a Heroic Farce" and "On Baile's Strand" are included in those collections. According to Wikipedia: "William Butler Yeats (13 June 1865 - 28 January 1939) was an Irish poet, dramatist, and one of the foremost figures of 20th century literature. A pillar of both the Irish and British literary establishments, in his later years Yeats served as an Irish Senator for two terms. He was a driving force behind the Irish Literary Revival, and along with Lady Gregory and Edward Martyn founded the Abbey Theatre, serving as its chief during its early years. In 1923, he was awarded a Nobel Prize in Literature for what the Nobel Committee described as "inspired poetry, which in a highly artistic form gives expression to the spirit of a whole nation." He was the first Irishman so honored. Yeats is generally considered one of the few writers whose greatest works were completed after being awarded the Nobel Prize; such works include The Tower (1928) and The Winding Stair and Other Poems (1929). Yeats was born and educated in Dublin, but spent his childhood in County Sligo. He studied poetry in his youth, and from an early age was fascinated by both Irish legends and the occult. Those topics feature in the first phase of his work, which lasted roughly until the turn of the century. His earliest volume of verse was published in 1889, and those slowly paced and lyrical poems display debts to Edmund Spenser and Percy Bysshe Shelley, as well as to the lyricism of the Pre-Raphaelite poets. From 1900, Yeats' poetry grew more physical and realistic. He largely renounced the transcendental beliefs of his youth, though he remained preoccupied with physical and spiritual masks, as well as with cyclical theories of life."

Hernani
¥8.09
1411/5000 Le drame classique a d'abord joué et publié en 1830. La pièce elle-même est en fran?ais, mais l'introduction est en anglais. Selon Wikipedia: ? Hernani est un drame du poète fran?ais Victor Hugo Le jeu est ouvert à Paris le 25 Février, 1830 Aujourd'hui est le drame pour les manifestations qui ont accompagné la première, et pour l'opéra de Verdi Ernani l'inspiration que pour son .. mérites est ... Victor-Marie Hugo (26 Février 1802-1822 mai 1885) était un poète fran?ais, auteur dramatique, romancier, essayiste, artiste plasticien, homme d'?tat, des militants des droits de l'homme et des représentants du mouvement romantique en France en France, Hugo est littéraire renommée principalement de ses poèmes, mais aussi de ses romans et ses Leistungen.Von dramatique de nombreux livres de poésie sont Contemplations et la Légende des particulièrement élevé en siècle le prestige et Hugo parfois, il est considéré comme le plus grand poète fran?ais, ses ?uvres les plus célèbres hors de France les romans Les Misérables et Notre-Dame de Paris (aussi connu comme le bossu de Notre-Dame) royal quand il était jeune, Hugo est devenu plus libéral que les décennies passées; il est devenu un partisan passionné de républicanisme, et son travail touche les questions les plus politiques et sociales et les tendances artistiques de son époque. Il est enterré au Panthéon. "

Le Roi S'Amuse
¥8.09
Drame classique dans le texte original, publié en 1832. Selon Wikipedia: "Victor-Marie Hugo (26 février 1802 - 22 mai 1885) était un poète, dramaturge, romancier, essayiste, artiste visuel, homme d'?tat, militant des droits de l'homme et En France, la renommée littéraire de Hugo vient en premier lieu de sa poésie, mais repose aussi sur ses romans et ses réalisations dramatiques Parmi les nombreux volumes de poésie, Les Contemplations et La Légende des siècles tiennent particulièrement haut dans l'estime critique, et Hugo est parfois identifié comme le plus grand poète fran?ais.A l'extérieur de la France, ses ?uvres les plus connues sont les romans Les Misérables et Notre-Dame de Paris (connu aussi en anglais sous le nom de Le Bossu de Notre Dame). était jeune, Hugo devint plus libéral au fil des décennies, il devint un partisan passionné du républicanisme et son travail touche à la plupart des questions politiques et sociales et aux tendances artistiques de son temps. Il est enterré au Panthéon. "

The Poems of Jonathan Swift
¥8.09
According to Wikipedia: "Jonathan Swift (30 November 1667 – 19 October 1745) was an Anglo-Irish satirist, essayist, political pamphleteer (first for the Whigs, then for the Tories), poet and cleric who became Dean of St. Patrick's Cathedral, Dublin. He is remembered for works such as Gulliver's Travels, A Modest Proposal, A Journal to Stella, Drapier's Letters, The Battle of the Books, An Argument Against Abolishing Christianity, and A Tale of a Tub. Swift is probably the foremost prose satirist in the English language, and is less well known for his poetry. Swift originally published all of his works under pseudonyms—such as Lemuel Gulliver, Isaac Bickerstaff, M.B. Drapier—or anonymously. He is also known for being a master of two styles of satire: the Horatian and Juvenalian styles."

A Woman of No Importance
¥8.09
Classic play. According to Wikipedia: "Oscar Fingal O'Flahertie Wills Wilde (1854 - 1900) was an Irish playwright, novelist, poet, and author of short stories. Known for his barbed wit, he was one of the most successful playwrights of late Victorian London, and one of the greatest celebrities of his day. As the result of a famous trial, he suffered a dramatic downfall and was imprisoned for two years of hard labour after being convicted of the offence of 'gross indecency.'"

La Esmeralda
¥8.09
Pièce classique / livret de Hugo, basé sur une scène de son roman Notre Dame de Paris (Le Bossu de Notre Dame), en fran?ais original. Selon Wikipedia: "Victor-Marie Hugo (26 février 1802 - 22 mai 1885) était un poète, dramaturge, romancier, essayiste, artiste visuel, homme d'?tat, militant des droits de l'homme et représentant du mouvement romantique en France. La renommée littéraire vient d'abord de sa poésie, mais repose aussi sur ses romans et ses réalisations dramatiques Parmi les nombreux volumes de poésie, Les Contemplations et La Légende des siècles sont particulièrement estimés et Hugo est parfois identifié comme le plus grand poète fran?ais. La France, ses ?uvres les plus connues sont les romans Les Misérables et Notre-Dame de Paris (connu aussi en anglais sous le titre de Le Bossu de Notre-Dame), bien que conservateur conservateur dans sa jeunesse, Hugo devint plus libéral au fil des décennies. il est devenu un partisan passionné du républicanisme et son travail touche à la plupart des questions politiques et sociales et aux tendances artistiques de son temps: il est enterré au Panthéon.

Shakespeare's Works: 37 plays, plus poetry, with line numbers
¥8.09
This file includes all of Shakespeare's plays, with line numbers (11 tragedies, 12 comedies, 10 histories, and 4 romances), plus his poetry (Sonnets, Venus and Adonis, Rape of Lucrece, Lover's Complaint, and Passionate Pilgrim. According to Wikipedia: "William Shakespeare (baptised 26 April 1564 – died 23 April 1616) was an English poet and playwright, widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's national poet and the "Bard of Avon" (or simply "The Bard"). His surviving works consist of 38 plays, 154 sonnets, two long narrative poems, and several other poems. His plays have been translated into every major living language, and are performed more often than those of any other playwright."

Constable
¥8.09
Biography, with 12 illustrations, from the series Masterpieces in Colour. According to Wikipedia: "John Constable (11 June 1776 – 31 March 1837) was an English Romantic painter. Born in Suffolk, he is known principally for his landscape paintings of Dedham Vale, the area surrounding his home—now known as "Constable Country"—which he invested with an intensity of affection. "I should paint my own places best", he wrote to his friend John Fisher in 1821, "painting is but another word for feeling". His most famous paintings include Dedham Vale of 1802 and The Hay Wain of 1821. Although his paintings are now among the most popular and valuable in British art, he was never financially successful and did not become a member of the establishment until he was elected to the Royal Academy at the age of 52. He sold more paintings in France than in his native England."

The Duchess of Padua
¥8.09
Play. According to Wikipedia: "Oscar Fingal O'Flahertie Wills Wilde (1854 - 1900) was an Irish playwright, novelist, poet, and author of short stories. Known for his barbed wit, he was one of the most successful playwrights of late Victorian London, and one of the greatest celebrities of his day. As the result of a famous trial, he suffered a dramatic downfall and was imprisoned for two years of hard labour after being convicted of the offence of 'gross indecency.'"

New Poems
¥8.09
Poetry collection. According to Wikipedia: "Robert Louis (Balfour) Stevenson ( 1850 - 1894), was a Scottish novelist, poet, and travel writer, and a leading representative of Neo-romanticism in English literature. He was the man who "seemed to pick the right word up on the point of his pen, like a man playing spillikins", as G. K. Chesterton put it. He was also greatly admired by many authors, including Jorge Luis Borges, Ernest Hemingway, Rudyard Kipling, Vladimir Nabokov, and J. M. Barrie. Most modernist writers dismissed him, however, because he was popular and did not write within their definition of modernism. It is only recently that critics have begun to look beyond Stevenson's popularity and allow him a place in the canon."

King John, with line numbers
¥8.09
The classic Shakespeare history play, with line numbers. According to Wikipedia: "The Life and Death of King John, a history play by William Shakespeare, dramatises the reign of John, King of England (ruled 1199–1216), son of Henry II of England and Eleanor of Aquitaine and father of Henry III of England. It is believed to have been written in the mid-1590s but was not published until it appeared in the First Folio in 1623."

Titus Andronicus in French
¥8.09
Traduit par Fran?ois Pierre Guillaume Guizot (1787 - 1874), historien fran?ais et homme d'?tat. Publié en 1864. Selon Wikipedia: "Titus Andronicus est une tragédie par William Shakespeare, et peut-être George Peele, censé avoir été écrit entre 1588 et 1593. Il est considéré comme la première tragédie de Shakespeare, et est souvent considéré comme sa tentative de imiter les scènes de vengeance violentes et sanglantes de ses contemporains, qui étaient extrêmement populaires auprès du public tout au long du XVIe siècle.La pièce se déroule pendant les derniers jours de l'Empire romain et raconte l'histoire fictive de Titus, un général de l'armée romaine, qui est engagé dans un cycle de vengeance avec Tamora, reine des Goths, c'est l'?uvre la plus sanglante et la plus violente de Shakespeare et traditionnellement l'une de ses pièces les moins respectées. "

Measure for Measure/ Maass fur Maass: Bilingual edition
¥8.09
Bilingual, English and German. Shakespeare comedy in English with line numbers and translated to German. According to Wikipedia: "Measure for Measure is a play by William Shakespeare, believed to have been written in 1603 or 1604. It was (and continues to be) classified as comedy, but its mood defies those expectations. As a result and for a variety of reasons, some critics have labelled it as one of Shakespeare's problem plays. Originally published in the First Folio of 1623 (where it was first labelled as a comedy), the play's first recorded performance was in 1604. The play deals with the issues of mercy, justice, and truth and their relationship to pride and humility: "Some rise by sin, and some by virtue fall". Zweisprachig, Englisch und Deutsch. Shakespeare-Kom?die in Englisch mit Zeilennummern und ins Deutsche übersetzt. Laut Wikipedia ist "Measure for Measure" ein Stück von William Shakespeare, das 1603 oder 1604 geschrieben wurde. Es wurde (und wird weiterhin) als Kom?die klassifiziert, aber seine Stimmung widersetzt sich diesen Erwartungen Eine Vielzahl von Gründen wurde von einigen Kritikern als eines von Shakespeares Problemspielen bezeichnet.Erst im First Folio von 1623 ver?ffentlicht (wo es zuerst als Kom?die bezeichnet wurde), war die erste Aufnahme des Stücks 1604. Das Stück handelt von den Themen von Barmherzigkeit, Gerechtigkeit und Wahrheit und ihrer Beziehung zu Stolz und Demut: "Einige erheben sich aus Sünde, und manche fallen durch Tugend".

Seven Plays
¥8.09
This collection includes the plays: The Duchess of Padua, An Ideal Husband, The Importance of Being Earnest, Lady Windermere's Fan, Salome, Vera, and A Woman of No Importance. According to Wikipedia: "Oscar Fingal O'Flahertie Wills Wilde (16 October 1854 – 30 November 1900) was an Irish writer and poet. After writing in different forms throughout the 1880s, he became one of London's most popular playwrights in the early 1890s. Today he is remembered for his epigrams, plays and the circumstances of his imprisonment, followed by his early death."

Measure for Measure, with line numbers
¥8.09
One of Shakespeare's "problem" plays. (Not quite a comedy, not quite a romance). According to Wikipedia: "Measure for Measure is a play by William Shakespeare, believed to have been written in 1603 or 1604. It was originally classified as a comedy, but is now also classified as one of Shakespeare's problem plays. Originally published in the First Folio of 1623, the play's first recorded performance was in 1604. The play deals with the issues of mercy, justice, truth and their relationship to pride and humility: "Some rise by sin, and some by virtue fall"

Five Plays
¥8.09
The Adulateur, a five-act play, published in 1773; The Defeat, excerpts from a play, published 1773; The Group, a three-act play, published in 1775; The Blockheads, a three-act play, published in 1776, shortly after the British withdrew from Boston The Motley Assembly, a farce, published in 1779. Mercy Warren (1728-1814) was sister of James Otis and wife of James Warren, both leaders in the early stages of the American Revolution. These plays of hers are of historical, not dramatic interest. Her main work is her history of the American Revolution (The Rise, Progress and Termination of the American Revolution Interspersed with Biographical, Political, and Moral Observations).

Milton's Poetical Works
¥8.09
Paradise Lost (1667), Paradise Regained (1671), Samson Agonistes (1671), and Minor Poems (1645). According to Wikipedia: "John Milton (December 9, 1608 ? November 8, 1674) was an English poet, prose polemicist, and civil servant for the Commonwealth of England. Most famed for his epic poem Paradise Lost, Milton is celebrated as well for his treatise condemning censorship, Areopagitica. Long considered the supreme English poet, Milton experienced a dip in popularity after attacks by T. S. Eliot and F. R. Leavis in the mid 20th century; but with multiple societies and scholarly journals devoted to his study, Milton's reputation remains as strong as ever in the 21st century."




 购物车
购物车 个人中心
个人中心



