
Soffio verso il cielo: Prova a soffiare anche tu
¥7.72
Soffio verso il cielo: Prova a soffiare anche tu

My Art Pieces And Thoughts
¥43.74
My Art Pieces And Thoughts

My Artworks And Thoughts
¥43.74
My Artworks And Thoughts

Letters of Capitulation
¥40.79
Letters of Capitulation

Ineffable
¥46.68
Ineffable

Songs of the Spirit: Hitherto Unpublished Poems and a Few Old Favorites
¥12.18
Songs of the Spirit: Hitherto Unpublished Poems and a Few Old Favorites
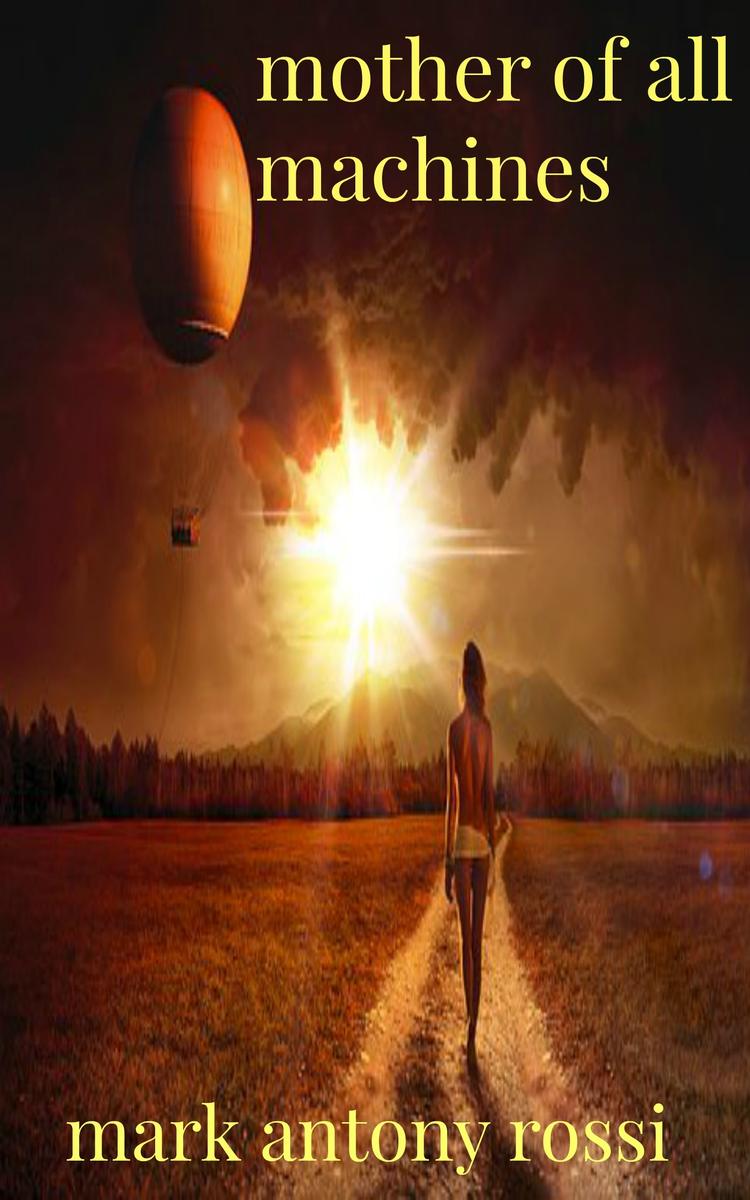

Mother of All Machines
¥16.27
Mother of All Machines

Catharsis
¥32.62
Catharsis

Metro Manila Mammal
¥24.44
Metro Manila Mammal

My World of Love and Happinness
¥32.62
My World of Love and Happinness

Beyond Pentatonics
¥40.79
Beyond Pentatonics

Anthony Van Dyck: Annotated Artworks
¥9.48
Anthony Van Dyck: Annotated Artworks

Musical Memories
¥8.09
Musical Memories
Piano Tuning
¥8.09
Piano Tuning

Chapters of Opera
¥8.09
Chapters of Opera
Songs from Books
¥8.09
Songs from Books

Poems
¥24.44
Poems

Haydn
¥8.09
Haydn

LIBERT? & POTERE. Saggio sull'arte di strisciare ad uso dei cortigiani
¥55.75
Exila?i este singura pies? scris? de Joyce, unde ??i face manifest?, prin regulile speciei, predilec?ia pentru m??tile puse fiec?rui personaj. Citit? ca o trecere ?n ordine cronologic? de la Portret al artistului ?n tinere?e la Ulise, piesa con?ine m?rci clare ale obsesiilor scriitorului ?i urme vizibile ale experien?ei omului James Joyce. Rela?iile de dragoste, parentale sau de prietenie sunt cele care dezechilibreaz? personajele, exilul temporar ?n Italia fiind doar o alt? form? a ?nstr?in?rii din Irlanda natal?.

La Songe d'une Nuit de'Ete (A Midsummer Night's Dream in French)
¥8.09
Comédie de Shakespeare, traduite en fran?ais par Fran?ois Pierre Guillaume Guizot (1787 - 1874), historien fran?ais et homme d'?tat. Publié en 1862. Selon Wikipedia: "Un Songe d'une nuit d'été est une pièce écrite par William Shakespeare, qui aurait été écrite entre 1590 et 1596. Elle décrit les événements entourant le mariage du duc d'Athènes, Thésée, et la Reine des Amazones, Hippolyta, dont les aventures de quatre jeunes amants athéniens et d'un groupe de six comédiens amateurs manipulés par les fées qui peuplent la forêt où se déroule la plus grande partie de la pièce. Les ?uvres les plus populaires de Shakespeare pour la scène et sont largement jouées à travers le monde. "

Troilus et Cressida, Troilus and Cressida in French
¥8.09
Traduit par Fran?ois Pierre Guillaume Guizot (1787 - 1874), historien fran?ais et homme d'?tat. Publié en 1862. Selon Wikipedia: "Troilus et Cressida est une tragédie de William Shakespeare, qui aurait été écrite en 1602. Il a également été décrit par Frederick S. Boas comme l'une des pièces à problèmes de Shakespeare. note avec la mort du noble cheval de Troie Hector et la destruction de l'amour entre Tro?lus et Cressida.Tout au long de la pièce, le ton s'écroule follement entre comédie débile et tristesse tragique, et les lecteurs et les spectateurs ont souvent du mal à comprendre comment on est Cependant, plusieurs éléments caractéristiques de la pièce (le plus notable étant sa remise en question constante de valeurs intrinsèques telles que la hiérarchie, l'honneur et l'amour) ont souvent été considérés comme nettement ?modernes? ..




 购物车
购物车 个人中心
个人中心



