
In the Footsteps of Hemingway From Pamplona to Bimini
¥10.30
Ernest Hemingway casts a very long shadow – especially the one thrown over Ray Knight by the Bahamian sunset on Hemingway’s beloved islands of Bimini. Using the late literary giant’s terse aphorisms and mordant quips as springboards for his own lean and drum-tight prose, Ray Knight invites us to join him on a journey from Pamplona to Bimini, in the footsteps of his literary hero. This collection of short stories, anecdotes and excerpts from the author’s novels runs the gamut of emotions, from pathos and tragedy to humor and unabashed sentimentality – from a moving and thought-provoking look at the ethical ramifications of euthanasia to a boxing tale that pulls no punches, and without which no homage to Hemingway would be complete. Whether you add an extra kick to your coffee break one tale at a time or settle down with a glass of rum and spend an evening ‘In The Footsteps of Hemingway’, you’re in for an enjoyable and edifying read – and a great introduction to the author’s full-length works. The Vet’s Dilemma:- A personal look at one man’s anguished choice between humanity and morality. What will he do? What would you do? The Tears of a Clown:- A clown’s antics bring joy to thousands of children but behind the make-up is a face racked with pain. Monty:- A man’s relationship with his car confounds his daughter and leads to a traumatic and deadly conclusion.. Shadows :- A man struggles for survival in a harsh and dangerous environment. Voices from his past come to haunt him. Will they save or condemn him? A Father’s Love:- A father risks the wrath of his community and his life in a desperate attempt rescue his son from the horror of addiction. It Tolls for Thee:- A washed-up boxer is offered one last, desperate shot at the big time – will he risk his life for one final chance of glory? Right of Passage:- A young hunter faces the ultimate test – will he become a legend or just a memory? A sample chapter from ‘The Mountain’… Felicia’s Cabin:- A kidnapped woman faces up to her captors in this sample chapter from’ The Hatcher File’… Walking With the Bulls:- The author recalls his experience in Pamplona in 1977 – a year of tragic events at the Festival of San Fermin Every Job in Town:- An amusing recollection of the author’s time in Sydney during 1980, when Australia was a land full of opportunities for a young man… either to get rich or get into a lot trouble!

A Portrait of the Artist as a Young Man
¥8.09
This unique edition of A Portrait of the Artist as a Young Man from Dead Dodo Vintage includes the full original text as well as exclusive features not available in other editions.
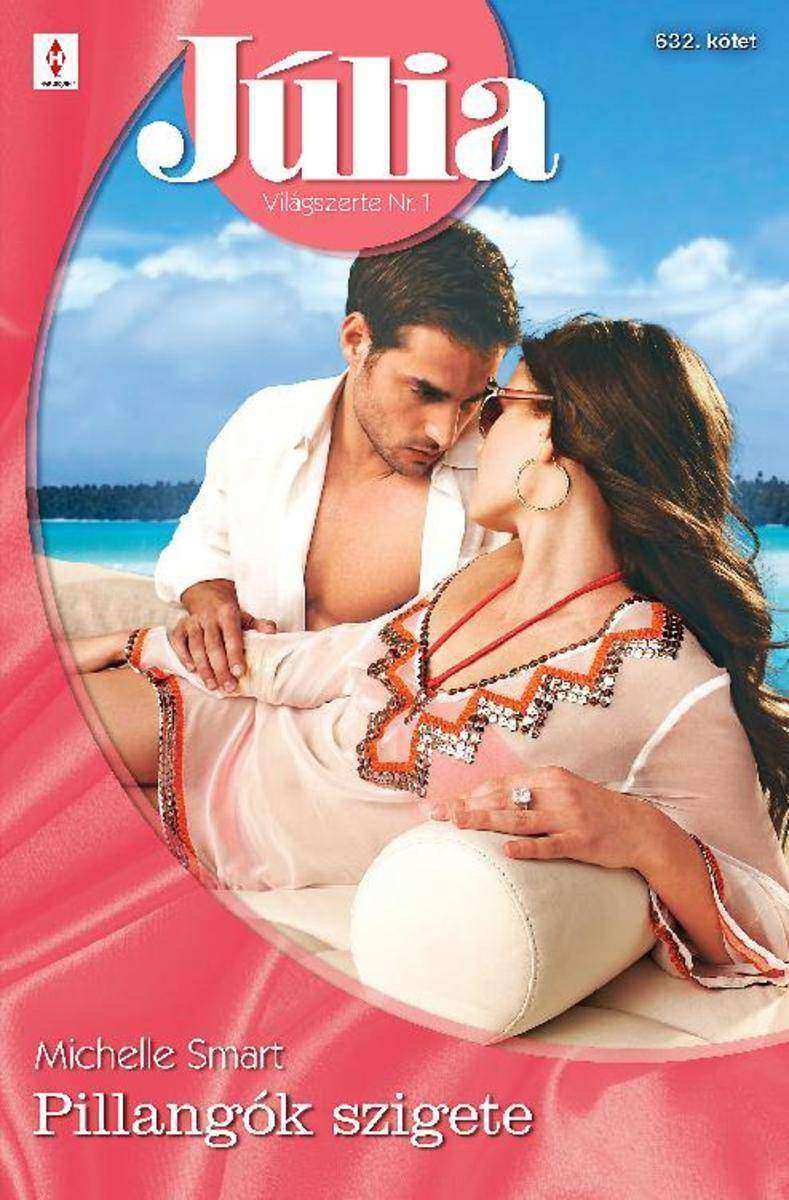

Pillangók szigete
¥20.36
Pillangók szigete

Engedetlen arajel?lt
¥20.36
Engedetlen arajel?lt

Szívhang 564–565. - Szívz?r
¥40.79
Szívhang 564–565. - Szívz?r
Utolsó lélegzetig
¥101.78
Utolsó lélegzetig

Veled Párizsban
¥20.36
Veled Párizsban
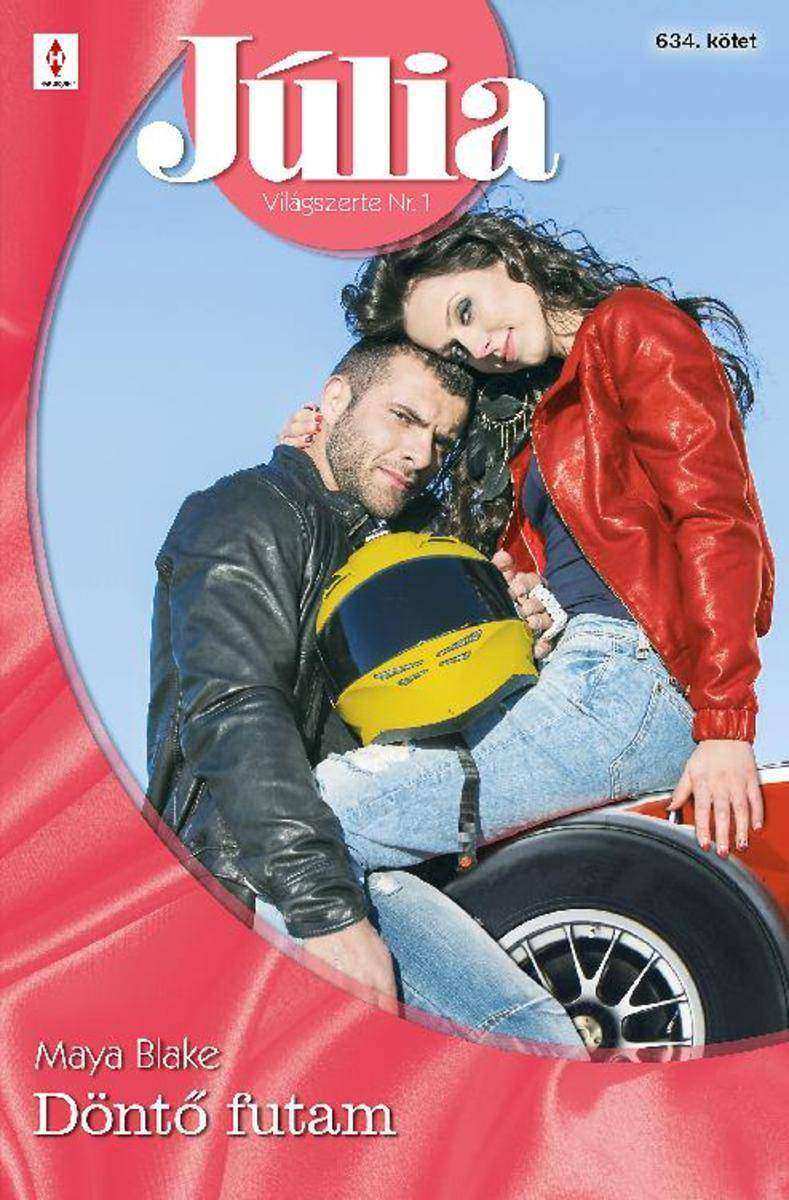

D?nt? futam
¥20.36
D?nt? futam

Naplemente a Central Parkban
¥87.23
Naplemente a Central Parkban

Túszejtés orosz módra
¥20.11
Túszejtés orosz módra

Felhívás kering?re, Bagoly és pacsirta: Bianca 309–310.
¥48.97
Felhívás kering?re, Bagoly és pacsirta: Bianca 309–310.

A birodalom ?r?k?se
¥20.11
A birodalom ?r?k?se

?s a mese valósággá válik…
¥20.52
s a mese valósággá válik…

Tigris vagy medúza?
¥20.52
Tigris vagy medúza?

Boldogság családi csomagolásban
¥46.60
Boldogság családi csomagolásban

Titkos küldetés, Dupla ?r?m, ?j fészek
¥46.60
Titkos küldetés, Dupla ?r?m, ?j fészek

A Prisoner
¥40.79
An officer by the name of Jilin served in the army in the Caucasus. One day he received a letter from home. It was from his mother, who wrote, 'I am getting old now, and I want to see my beloved son before I die. Come and say good-bye to me, and when you have buried me, with God’s grace, you can return to the Army. I have found a nice girl for you to marry; she is clever and pretty, and has some property of her own. If you like her perhaps you will marry and settle down for good.'

Three Questions and Other Tales
¥40.79
It once occurred to a King that if he knew the right moment when to begin on any work and the right kind of people to have or not to have dealings with and the thing to do that was more important than any other thing, he would always be successful. And he proclaimed throughout his kingdom that he would give a great reward to any one who could tell him what was the right moment for any action, and who were the most essential of all people, and what was the most essential thing of all to do.

Sherlock: Complete Novels
¥40.79
Sherlock, one of the greatest detectives of all time. This Fractal Press edition features complete collection of the four Sherlock Holmes novels, including: A Study in Scarlet, The Sign of the Four, The Hound of the Baskervilles, The Valley of Fear.

A Voyage to the Country of the Houyhnhnms
¥40.79
Gulliver sets out as captain of a ship, but after the mutiny of his crew and a long confinement in his cabin, he arrives in an unknown land. This land is populated by Houyhnhnms, rational-thinking horses who rule, and by Yahoos, brutish humanlike creatures who serve the Houyhnhnms. Gulliver sets about learning their language, and when he can speak he narrates his voyages to them and explains the constitution of England. He is treated with great courtesy and kindness by the horses and is enlightened by his many conversations with them and by his exposure to their noble culture.

The Essential Epicurus
¥40.79
For Epicurus, the purpose of philosophy was to attain the happy, tranquil life, characterized by peace and freedom from fear, the absence of pain, and by living a self-sufficient life surrounded by friends. He taught that pleasure and pain are the measures of what is good and evil; death is the end of both body and soul and should therefore not be feared; the gods neither reward nor punish humans; the universe is infinite and eternal; and events in the world are ultimately based on the motions and interactions of atoms. Although much of Epicurus' written work has been lost, the remaining principle doctrines and his letters featured in this book provide an insight into the Epicurean school of thought, which was originally based in the garden of his house and thus called The Garden.




 购物车
购物车 个人中心
个人中心



